Introduction:
4 Levels of Cognitive Rehabilitation: Restoring Minds and Lives
What Is Cognitive Rehabilitation?

Cognitive rehabilitation is a therapeutic approach designed to improve cognitive functions that may have been affected by injury, illness, or other neurological conditions. The goal is to enhance cognitive abilities such as memory, attention, problem-solving, and decision-making. This type of rehabilitation is often employed for individuals who have experienced brain injuries, strokes, or neurological disorders.
Cognitive rehabilitation programs are tailored to the specific needs and challenges of each individual. They typically involve a combination of exercises, activities, and strategies aimed at promoting neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to reorganize and adapt by forming new neural connections.
Examples of cognitive rehabilitation interventions may include memory exercises, attention training, problem-solving tasks, and activities that improve executive functions. Speech and language therapy, occupational therapy, and physical therapy may also be components of a comprehensive cognitive rehabilitation program, depending on the nature of the cognitive difficulties.
The ultimate objective of cognitive rehabilitation is to help individuals regain or improve their cognitive abilities, enhance their independence, and optimize their overall quality of life. The effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation can vary based on the severity of the cognitive impairment and the individual’s response to the interventions.
what are the 4 levels of cognitive rehabilitation per the World Health Organization
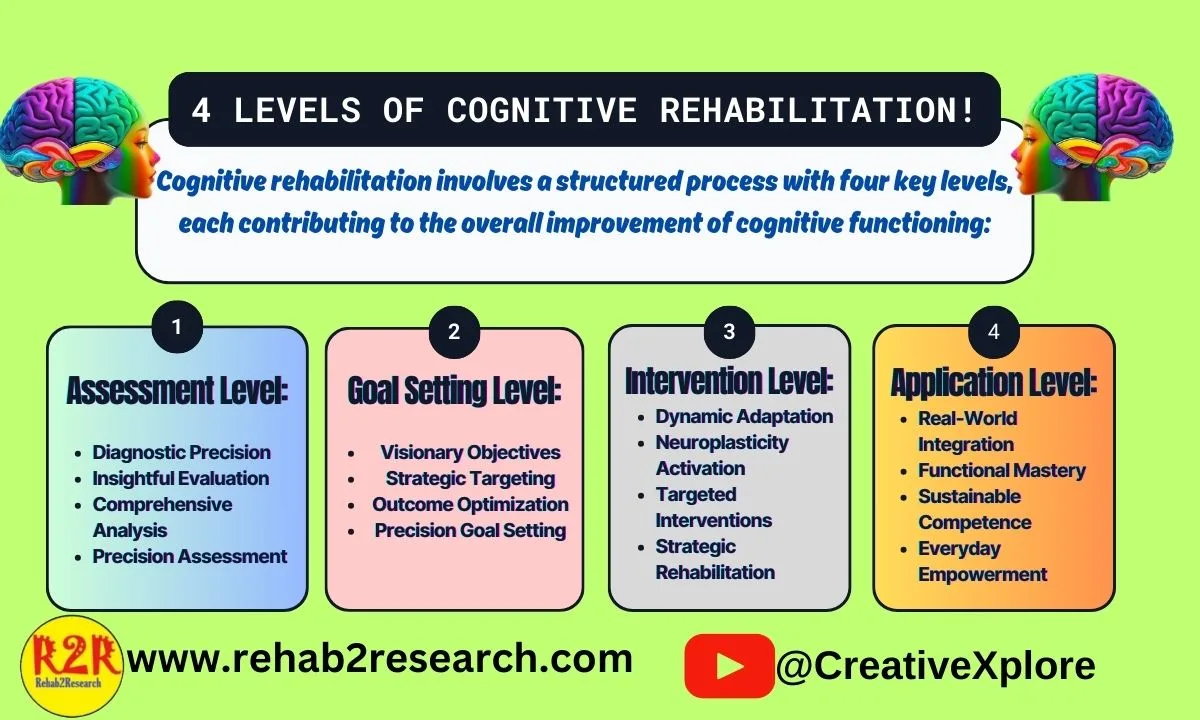
Cognitive rehabilitation involves a structured process with four key levels, each contributing to the overall improvement of cognitive functioning:
1. Assessment Level:
This initial stage involves a thorough evaluation of an individual’s cognitive strengths and weaknesses. Through diagnostic precision and insightful analysis, healthcare professionals identify specific areas of impairment, laying the foundation for a targeted rehabilitation plan.
- Diagnostic Precision
- Insightful Evaluation
- Comprehensive Analysis
- Precision Assessment
2. Goal Setting Level:
Building upon the assessment, this level focuses on establishing visionary objectives tailored to the individual’s needs. Strategic targeting and precision goal setting guide the formulation of clear, measurable goals, providing a roadmap for the rehabilitation journey.
- Visionary Objectives
- Strategic Targeting
- Outcome Optimization
- Precision Goal Setting
3. Intervention Level:
At this stage, targeted interventions come into play. Activation of neuroplasticity, dynamic adaptation, and strategic rehabilitation efforts are employed. These interventions include personalized exercises, activities, and strategies designed to address and improve specific cognitive functions identified during assessment.
- Dynamic Adaptation
- Neuroplasticity Activation
- Targeted Interventions
- Strategic Rehabilitation
4. Application Level:
The final level emphasizes the real-world application of acquired cognitive skills. Individuals engage in activities that promote functional mastery, sustainable competence, and everyday empowerment. This level aims to seamlessly integrate improved cognitive functioning into daily life, enhancing independence and overall quality of life.
- Real-World Integration
- Functional Mastery
- Sustainable Competence
- Everyday Empowerment
These four levels form a cohesive framework for cognitive rehabilitation, offering a systematic approach to address cognitive challenges and promote lasting improvements in various aspects of an individual’s life.
What happens in cognitive rehab?
Cognitive rehabilitation involves a structured and personalized set of activities and exercises to address and improve specific cognitive functions that may be impaired due to injury, illness, or neurological conditions. The process typically includes the following components:
- Assessment: A comprehensive evaluation is conducted to assess the individual’s cognitive strengths and weaknesses. This may involve various cognitive tests, interviews, and observations to identify specific areas of impairment.
- Goal Setting: Based on the assessment, specific cognitive goals are established. These goals are tailored to the individual’s needs and may focus on improving memory, attention, problem-solving, language skills, or other cognitive functions.
- Individualized Interventions: Cognitive rehabilitation programs are customized to target the identified cognitive deficits. Activities and exercises may include memory drills, attention training exercises, problem-solving tasks, and activities that promote executive functions.
- Repetition and Practice: Repetition is a key element in cognitive rehabilitation. Regular practice of targeted activities helps reinforce neural pathways and encourages neuroplasticity, allowing the brain to adapt and improve cognitive functioning.
- Use of Strategies: Individuals are taught cognitive strategies and compensatory techniques to overcome challenges. These may include memory aids, organizational tools, and specific approaches to enhance cognitive skills in daily life.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Depending on the nature of the cognitive difficulties, cognitive rehabilitation may involve collaboration with other healthcare professionals such as speech therapists, occupational therapists, and physical therapists to address a range of cognitive and functional aspects.
- Feedback and Monitoring: Progress is regularly monitored, and feedback is provided to the individual. Adjustments to the rehabilitation program may be made based on the individual’s response and improvements.
- Real-world Application: The ultimate goal is to transfer the acquired cognitive skills to real-world situations. This may involve practicing tasks related to daily activities, work, or social interactions to enhance functional independence.
Cognitive rehabilitation is a dynamic and evolving process that requires ongoing assessment and adjustment to meet the changing needs of the individual. The duration and intensity of cognitive rehabilitation programs can vary depending on the severity of cognitive impairment and the individual’s progress.
4 Levels of Cognitive Rehabilitation
What to know about cognitive rehabilitation therapy
Your Guide to Cognitive Rehabilitation
Benefits of cognitive rehabilitation
Cognitive rehabilitation offers a range of benefits for individuals who have experienced cognitive impairments due to injuries, illnesses, or neurological conditions. Some of the key benefits include:
- Improved Cognitive Functioning: The primary goal of cognitive rehabilitation is to enhance cognitive abilities such as memory, attention, problem-solving, and decision-making. Individuals may experience improvements in these areas, leading to enhanced overall cognitive functioning.
- Increased Independence: As cognitive abilities improve, individuals often gain greater independence in their daily lives. They may become more proficient in managing tasks, making decisions, and participating in various activities without as much assistance.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Cognitive rehabilitation aims to optimize an individual’s overall quality of life by addressing cognitive challenges. Improved cognitive functioning can positively impact social interactions, relationships, work performance, and overall well-being.
- Adaptation and Compensation: Individuals are taught strategies and techniques to adapt to and compensate for cognitive deficits. These compensatory strategies can empower individuals to navigate challenges more effectively and maintain a higher level of functioning.
- Increased Confidence and Self-Esteem: Successfully overcoming cognitive challenges through rehabilitation can boost an individual’s confidence and self-esteem. Achieving cognitive milestones and gaining a sense of mastery over tasks contribute to a more positive self-perception.
- Enhanced Social Participation: Improved cognitive functioning can facilitate better communication and social interactions. This, in turn, can lead to increased participation in social activities, strengthening relationships and reducing social isolation.
- Functional Independence: Cognitive rehabilitation often focuses on real-world application, helping individuals apply newly acquired cognitive skills to daily activities. This promotes functional independence and the ability to perform tasks relevant to work, home, and community settings.
- Optimized Work Performance: For individuals returning to work after cognitive challenges, cognitive rehabilitation can contribute to improved work performance. This may involve regaining skills related to concentration, problem-solving, and task management.
- Long-Term Benefits: The effects of cognitive rehabilitation can extend beyond the duration of the program. By promoting neuroplasticity, individuals may continue to experience improvements over time, even after the formal rehabilitation period.
- Quality of Care and Support: Engaging in cognitive rehabilitation often involves working with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals. This collaborative approach ensures comprehensive care and support, addressing various aspects of an individual’s cognitive and emotional well-being.
It’s important to note that the benefits of cognitive rehabilitation can vary depending on the individual’s specific condition, the severity of cognitive impairment, and other factors. The effectiveness of rehabilitation is often influenced by factors such as early intervention, individual motivation, and ongoing support.
What is cognitive rehabilitation used for?
Cognitive rehabilitation is used for addressing and improving cognitive deficits resulting from various conditions, injuries, or illnesses. Some common applications include:
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): Cognitive rehabilitation is frequently employed to help individuals recovering from traumatic brain injuries. It aims to restore cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and problem-solving that may be impaired due to the injury.
- Stroke: Individuals who have suffered a stroke may experience cognitive impairments. Cognitive rehabilitation is used to assist in the recovery of skills such as language, memory, and spatial awareness affected by stroke-related damage to the brain.
- Neurological Disorders: Conditions such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease can lead to cognitive challenges. Cognitive rehabilitation is utilized to manage and improve cognitive functions, enhancing the individual’s ability to cope with the effects of these disorders.
- Concussions: After a concussion or mild traumatic brain injury, individuals may experience cognitive difficulties. Cognitive rehabilitation helps in the recovery process by addressing issues like concentration, memory, and attention.
- Neuropsychiatric Conditions: Conditions like depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can impact cognitive functioning. Cognitive rehabilitation may be part of a comprehensive treatment plan to address cognitive symptoms associated with these mental health conditions.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Cognitive rehabilitation techniques may be used to improve executive functions, attention, and organizational skills in individuals with ADHD.
- Aging-Related Cognitive Decline: As individuals age, they may experience cognitive decline. Cognitive rehabilitation interventions can be employed to manage age-related cognitive changes and support cognitive health in older adults.
- Brain Tumors: Individuals who have undergone treatment for brain tumors may face cognitive challenges. Cognitive rehabilitation helps them regain cognitive abilities and adapt to changes in cognitive function.
- Substance Abuse and Addiction: Cognitive rehabilitation can be beneficial in addressing cognitive impairments associated with substance abuse and addiction. It may help individuals rebuild cognitive skills essential for daily functioning and recovery.
- Developmental Disorders: Children and adolescents with developmental disorders such as autism spectrum disorder or intellectual disabilities may benefit from cognitive rehabilitation to enhance cognitive and adaptive skills.
Cognitive rehabilitation is tailored to the specific needs of individuals and the nature of their cognitive challenges. It is a versatile and adaptive approach aimed at improving overall cognitive functioning and enhancing the quality of life for individuals facing cognitive impairments.
Conclusion
You May Also Like: 4 Levels of Cognitive Rehabilitation
Transform Your Life in 90 Days with Nova Care Rehabilitation
- How to Do Pulmonary Rehabilitation at Home
- Conditions or Injuries: What Types Can Benefit from Rehabilitation?
Occupational Rehabilitation Services: Empowering Recovery and Enhancing Well-being
Physical Therapy Equipment Insights: Elevating Wellness with the Latest Advancements
FAQs: 4 Levels of Cognitive Rehabilitation
How long does cognitive rehabilitation typically last?
Cognitive rehabilitation duration varies depending on individual needs but can last anywhere from a few months to several years.
Is cognitive rehabilitation suitable for all age groups?
Yes, cognitive rehabilitation can benefit individuals of all age groups, from children to the elderly.
Are there any side effects of cognitive rehabilitation?
Cognitive rehabilitation is generally safe and has minimal side effects. However, individual responses may vary.
Can cognitive rehabilitation completely restore cognitive functions?
While it can significantly improve cognitive abilities, complete restoration depends on the severity of the impairment and other factors.
Does insurance cover cognitive rehabilitation?
In many cases, cognitive rehabilitation may be covered by health insurance, but coverage can vary depending on the policy and the specific treatment plan.





Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Very interesting info!Perfect just what I was searching for!Raise blog range