Section 1
Demographic Shifts in Nepal:
Nepal is undergoing profound demographic shifts marked by a notable increase in its aging population. Over recent years, statistical data reveals a significant rise in the number of elderly citizens, reflecting a transformative trend. Factors such as improved healthcare and enhanced living conditions contribute to this demographic shift. Understanding these demographic changes is crucial for policymakers and stakeholders, guiding the development of targeted strategies and resources to address the evolving needs of an aging society. This demographic transition not only shapes the country’s population dynamics but also underscores the necessity of proactive measures to support and enhance the well-being of Nepal’s growing elderly population.

Section 2
Health Challenges Faced by Nepal’s Elderly:
Nepal’s elderly population encounters a spectrum of health challenges that demand attention and targeted interventions. Limited healthcare access stands as a prominent issue, exacerbated by geographic constraints and economic factors. Cultural norms play a role in shaping caregiving practices, impacting the overall well-being of the elderly. Common age-related health concerns, ranging from chronic diseases to mental health, pose additional challenges. Addressing these issues is crucial for the formulation of effective healthcare policies and support systems tailored to the unique needs of Nepal’s elderly citizens. It requires a comprehensive approach that acknowledges the diverse health challenges prevalent within this growing demographic.
Section 3
Societal and Cultural Factors:
Societal and cultural factors significantly influence the landscape of elderly care in Nepal. Traditional norms and values play a pivotal role in shaping the dynamics of familial and community support for the elderly. While these cultural elements often contribute positively to caregiving, they can also pose challenges, especially in rapidly changing societies. Examining how societal expectations impact elderly individuals and their families sheds light on potential areas for improvement. Balancing tradition with modern needs becomes essential to foster a supportive environment that respects cultural values while ensuring the well-being of Nepal’s aging population.
Section 4
Economic Implications:
The aging population in Nepal carries profound economic implications that ripple through various sectors. As the demographic landscape shifts, changes in the workforce dynamics become apparent. The increasing demand for healthcare services and support for the elderly places a considerable economic burden on both families and the broader healthcare system. Balancing the needs of an aging population with economic sustainability poses a challenge, requiring strategic planning and innovative solutions. Understanding these economic implications is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and communities to develop sustainable strategies that address the unique economic challenges associated with Nepal’s growing elderly demographic.
Section 5
Government Initiatives and Support Systems:
Nepal has implemented diverse government initiatives and support systems to address the specific needs of its aging population. These programs aim to provide healthcare, social assistance, and financial support to elderly citizens. Through targeted policies, the government seeks to enhance the overall well-being of the elderly, acknowledging the challenges they face. Evaluating the effectiveness of these initiatives is pivotal in ensuring that they align with the evolving needs of Nepal’s aging demographic. Government efforts, when well-directed and responsive, play a vital role in creating a supportive environment that fosters a dignified and healthy life for the
Section 6
Community Engagement and Solutions:
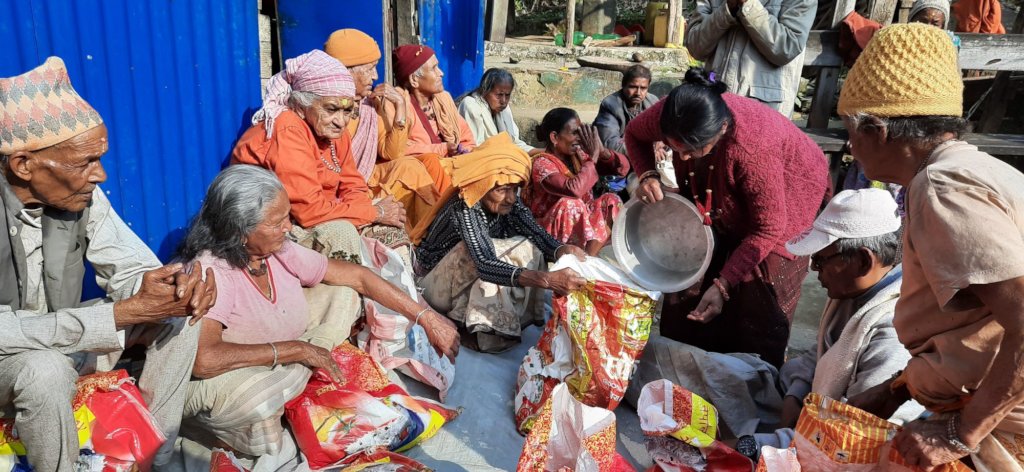
Community engagement is instrumental in crafting meaningful solutions to address the challenges posed by Nepal’s aging population. Local involvement fosters supportive networks, providing essential companionship and assistance for the elderly. Innovative community-driven solutions emerge, offering a more holistic approach to elderly care. From grassroots initiatives to collaborative efforts, community engagement becomes a cornerstone for promoting well-being and resilience among Nepal’s aging citizens. This collective approach not only acknowledges the unique needs of the elderly but also establishes a sense of shared responsibility, fostering a compassionate and inclusive society that values and supports its senior members.
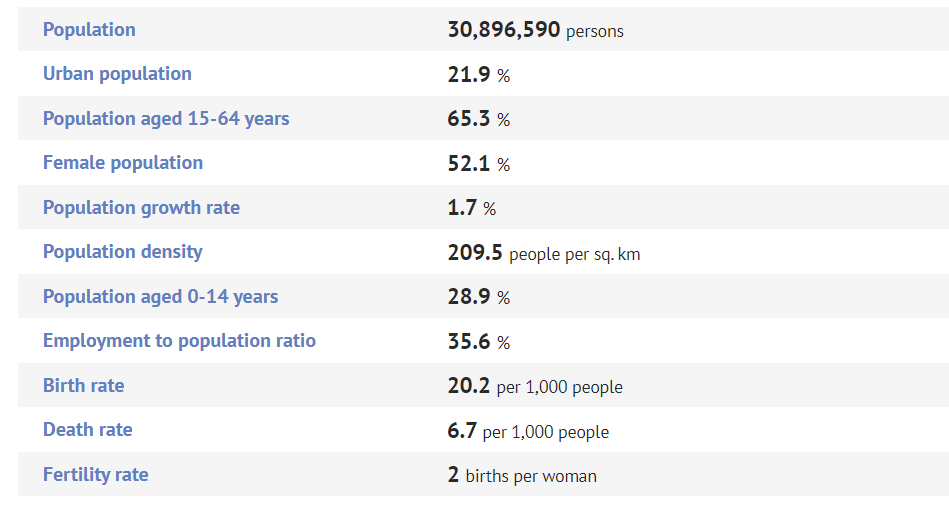
Population of Elderly people in Nepal:

Detail demographic Source: CBS Nepal 2021
Tableting data here
Conclusion of Nepal’s Aging Population
Summing up the key insights, this conclusion emphasizes the urgency of addressing the health impact on Nepal’s elderly population. A call to action encourages increased awareness, collaboration, and support, fostering a collective effort to improve the well-being of Nepal’s aging citizens.
In conclusion, the shifting demographics in Nepal demand urgent attention to the impact on elderly health. As the aging population grows, so does the need for targeted healthcare strategies and societal support. Addressing prevalent health challenges, economic implications, and government initiatives are crucial. Moreover, community engagement emerges as a vital force for positive change. The call to action is clear: heightened awareness, collaborative efforts, and sustained support are imperative to enhance the overall well-being of Nepal’s aging population. By embracing these challenges, we pave the way for a more compassionate and inclusive future for our senior population.
You May Also Like: Nepal’s Aging Population
FAQs: How Nepal’s Aging Population is Impacting Elderly Health
1. Why is Nepal’s aging population a significant concern for healthcare?
- The increasing elderly demographic poses unique health challenges, demanding specialized healthcare resources and strategies.
2. What are the prevalent health challenges faced by Nepal’s elderly?
- Common issues include limited healthcare access, cultural influences on caregiving, and a spectrum of age-related health concerns.
3. How does the aging population affect the economic landscape in Nepal?
- Changes in the workforce and increased healthcare demands contribute to economic implications, affecting both families and the broader system.
4. Are there government initiatives addressing the health needs of the elderly in Nepal?
- Yes, various programs exist, and this section explores their effectiveness in providing support and care to the aging population.
5. How can community engagement contribute to alleviating the impact on elderly health?
- Local involvement is crucial for creating supportive networks and innovative solutions, enhancing the overall well-being of Nepal’s elderly citizens.
6. What is the call to action proposed in addressing the challenges of Nepal’s aging population?
- The conclusion emphasizes the need for increased awareness, collaboration, and support to improve healthcare and societal conditions for the elderly.














Thank you I have just been searching for information approximately this topic for a while and yours is the best I have found out so far However what in regards to the bottom line Are you certain concerning the supply
I just could not leave your web site before suggesting that I really enjoyed the standard information a person supply to your visitors Is gonna be again steadily in order to check up on new posts
Ok thanks I will follow your suggestion.